The Department of State has released the visa bulletin for June 2020 outlining the availability of immigrant visa numbers for the upcoming month.
NOTE: Adjustment of Status Filing Charts June 2020
For Family-Sponsored Filings:
In the F2A category, there is a cutoff date on the Dates for Filing chart. However, the category is “current” on the Final Action Dates chart. This means that applicants in the F2A category may file for adjustment applications using the Final Action Dates chart for June 2020.
For all the other family-sponsored preference categories, you must use the Dates for Filing chart in the Department of State Visa Bulletin for June 2020.
For Employment-Based Preference Filings:
For all employment-based preference categories, you must use the Final Action Dates chart in the Department of State Visa Bulletin for June 2020.
June Visa Bulletin Cutoff Dates
Employment Based Categories
According to the Department of State’s June Visa Bulletin, the following cutoff dates will apply for the issuance of an immigrant visa for employment-based categories:
- EB-1: All countries remain current during the month of June except for China and India. EB-1 China moved forward by one month to August 15, 2017, while EB-1 India moved forward by more than 10 months to June 8, 2016.
- EB-2: All countries remain current during the month of June except for China and India. EB-2 China moved forward by one month to November 1, 2015, and India moved forward by 10 days to June 12, 2009.
- EB-3 Professional and Skilled Workers: All countries remain current except for India and China. Except for India and China all countries moved forward by more than ten months to November 8, 2017. Cutoff dates for China and India advanced by one month, with China moving ahead to June 15, 2016, and India moving ahead to April 1, 2009.
- EB-5: Most countries remain current. EB-5 China moved forward by two weeks to July 15, 2015; EB-5 India moved forward by three months to January 1, 2020; and Vietnam moved forward by three weeks to April 22, 2017.
Cutoff dates in the Dates for Filing Chart for June have remained mostly the same in comparison to the previous month, the only change is for EB-4 El Salvador, Honduras, and Guatemala which moved forward four and a half months to February 1, 2017. USCIS will accept adjustment applications based on the Final Action Dates chart for June 2020, the same as last month.
Final Action Dates Chart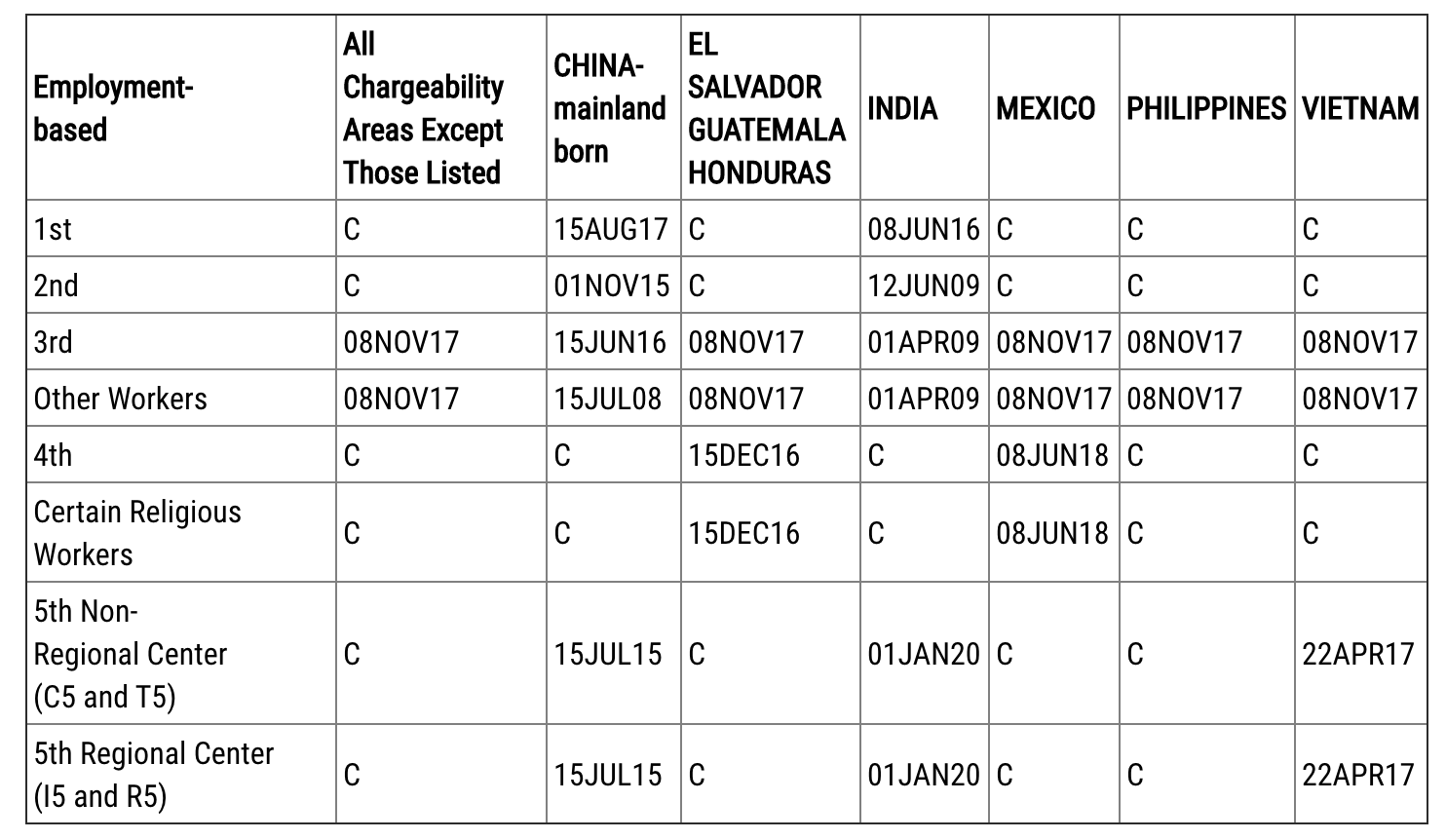
Family-Sponsored Categories
According to the Department of State’s June Visa Bulletin, the following cutoff dates will apply for the issuance of an immigrant visa for family-sponsored categories:
**Note only applicants in the F2A category may file using the Final Action Dates chart for June 2020 to file adjustment applications. All other family-sponsored preference categories must use the Dates for Filing chart.
Dates for Filing Chart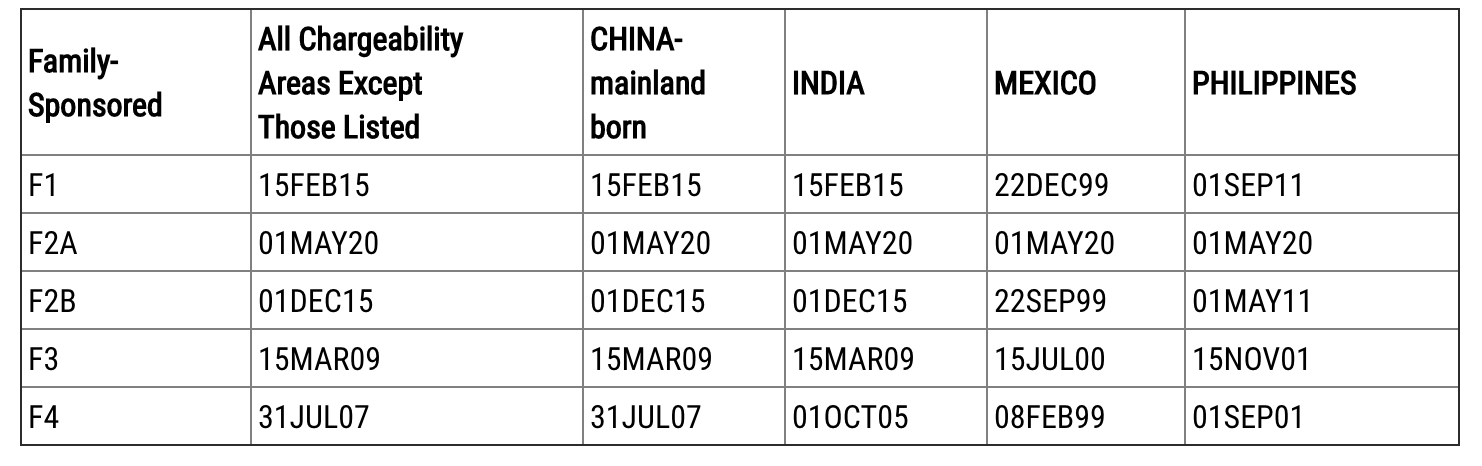
Alert Regarding the April 22nd Presidential Proclamation
As you may be aware President Trump’s April 22nd presidential proclamation suspends the issuance of immigrant visas at U.S. Consulates worldwide for certain classes of immigrants until June 22, 2020, assuming the proclamation is not extended beyond this date. As Consulates worldwide begin to reopen, consular officers will enforce the presidential proclamation by refusing immigrant visas to those who were outside of the United States as of 11:59 p.m. EDT on April 23, 2020, have not been issued an immigrant visa or similar U.S. travel document, and are not otherwise exempt from the proclamation. The following types of immigrants have been specifically exempted from the proclamation and are eligible for visa issuance in June:
- Applicants for EB-5 immigrant visas;
- Spouses of U.S. citizens;
- Children under 21 of U.S. citizens and prospective adoptees in the IR-4 or IH-4 visa classifications;
- Foreign nationals seeking to enter on an immigrant visa as a physician, nurse or other healthcare professional, as well as their spouse and unmarried children under 21;
- Foreign nationals whose entry would further important U.S. law enforcement objectives;
- Members of the U.S. armed forces and the spouses and children of such individuals;
- Foreign nationals seeking to enter as Special Immigrants in the SI or SQ classification, and the spouse and children of such individuals; and
- Foreign nationals whose entry is in the U.S. national interest.
Continue reading
 Visa Lawyer Blog
Visa Lawyer Blog















