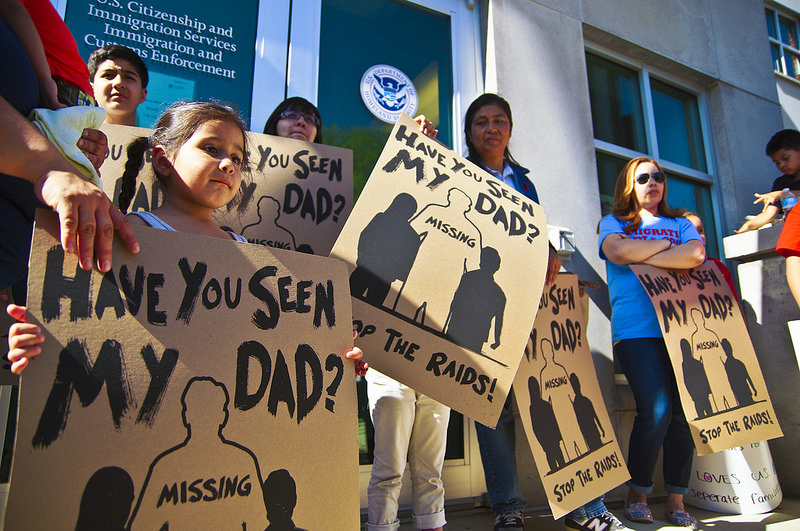
Today in a Seattle courtroom the Ninth Circuit Court of Appeals heard arguments on Trump’s revised travel ban. As you may recall President Trump issued a revised executive order in March to salvage his embattled travel ban, barring the entry of foreign nationals from Iran, Syria, Sudan, Libya, Somalia, and Yemen for a 90-day period and refugees for 120 days. For over an hour, a three-judge panel listened to arguments from the U.S. Solicitor General Jeffrey Wall arguing on behalf of the Trump administration and Neal Katyal, an attorney representing the state of Hawaii and individuals challenging the President’s revised travel ban. The three-judge panel included Judge Ronald Gould, a moderate judge from Seattle, Washington, Judge Michael Hawkins, a moderate to liberal judge from Phoenix, Arizona, and Judge Richard Paez a liberal judge from Pasadena, California. The central question before the court was whether the President’s revised travel ban amounts to a violation of the U.S. Constitution based on religious discrimination.
The mood in the courtroom was contentious. Judges probed the Solicitor General to determine whether the President’s revised travel ban was specifically aimed at Muslims. The Solicitor General argued that the executive order was neutrally worded and that there were no indications in the language of the President’s executive order to indicate that there was any intent to discriminate the Muslim population. In a heated exchange, liberal Judge Richard Paez countered that even if the President’s executive order was “neutrally worded,” taking a seemingly “neutral” stance does not mean an executive order is devoid of discriminatory intent. Judge Paez noted that the executive order that interned Japanese Americans during World War II was also neutrally worded given that there was no reference to Japanese people specifically, but that the President at the time did intend to discriminate that particular demographic. During oral argument, Judge Paez commented on remarks made by the President during his campaign which have indicated his intent to target Muslims specifically with his executive order. Paez stated that Trump made references to a Muslim ban “in the midst of a highly contentious campaign” raising questions about whether the court should consider taking that into account.
 Visa Lawyer Blog
Visa Lawyer Blog