Presently, the Employment and Training Administration’s (ETA) Office of Foreign Labor Certification (OFLC) is experiencing significant delays in processing employer H-2B certification applications. These delays are owed to various factors. The most important includes a mandatory 17-day certification pause that took place at the Chicago National Processing Center, for the purpose of implementing revisions of the H-2B prevailing wage and other standards required by law. Additionally, the OFLC announced that the amount of H-2B certification applications received has doubled in comparison to the previous year. Lastly, the electronic filing system iCERT, experienced significant technical problems, slowing the certification process down significantly for employers of H-2B workers. Unfortunately, these delays have diminished an employer’s ability to hire foreign workers during a time of need, and have had an adverse affect on small businesses who depend on these temporary and seasonal workers to perform work that cannot be readily filled by American workers.
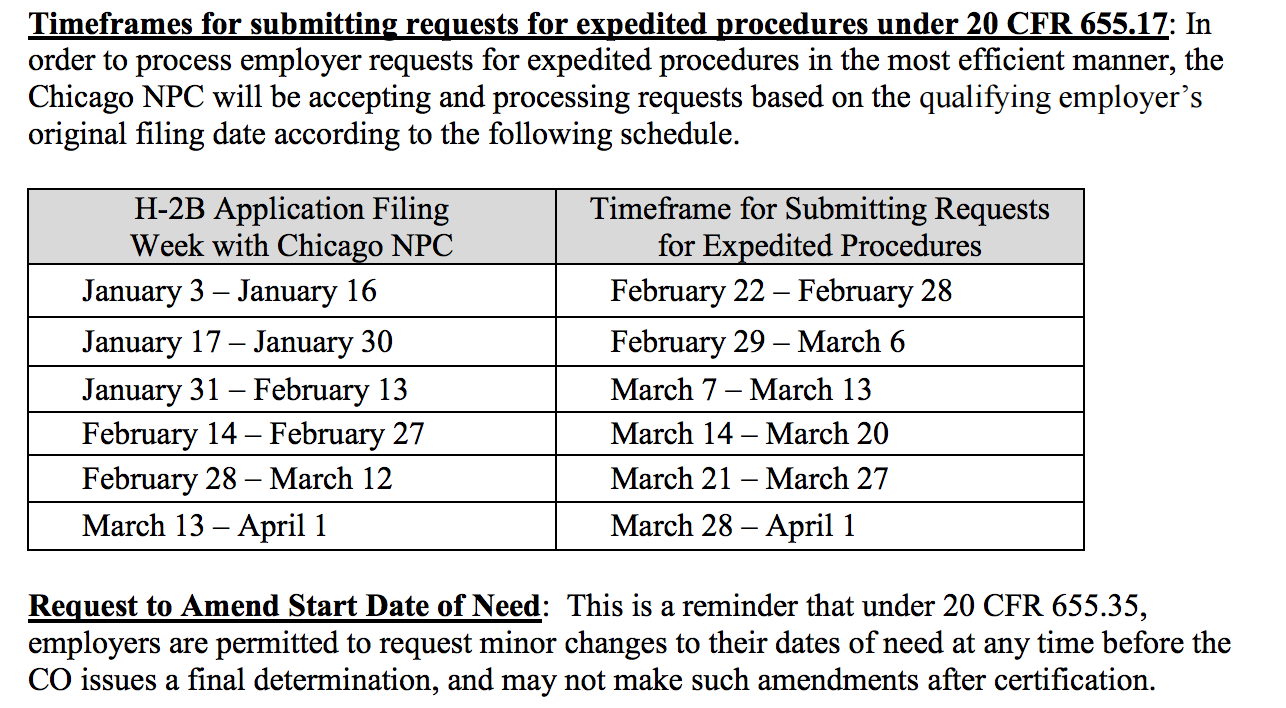
To alleviate the certification backlogs, the Chicago National Processing Center has announced that employers may file an emergency request for expeditious handling of their applications under 20 CFR 655.17.
Expeditious Requests for Emergency Procedures under 20 CFR 655.17:
- Based on the factors causing the backlogs, the OFLC has determined that employers are entitled to request expeditious emergency procedures for their currently pending applications for certification, under 20 CFR 655.17, on the basis of good and substantial cause. Emergency requests are warranted given that the backlogs caused by the delays in the application process are considered outside of the employers’ control, that employers have suffered unforeseen changes in market conditions because of the delays, amid a climate of uncertainty.
Employers with pending H-2B applications for certification must submit their expedite requests for emergency procedure, by email to the Chicago NPC at ER.H2B.Chicago@dol.gov beginning Monday February 22, 2016 (12:01 AM) through Friday April 1, 2016 (at 12:00 midnight). Requests may also be made by fax (312) 886-1688 or by US mail to:
ATTN: H-2B Request for Emergency Handling
U.S. Department of Labor ETA OFLC
Chicago NPC
11 West Quincy Court
Chicago, IL 60604-2105
The NPC may extend this emergency request period beyond April 1, however at this time no such extension has been announced. Filing a new H-2B application is not necessary for an expedite request.
Employers filing for emergency treatment under 20 CFR 655.17 must request that the pending application for certification and proposed job order be “incorporated by reference” into the request made under 20 CFR 655.17, and state the withdrawal of the prior application. The procedure for submitting an expedite requested will be listed below.
Continue reading

 Visa Lawyer Blog
Visa Lawyer Blog