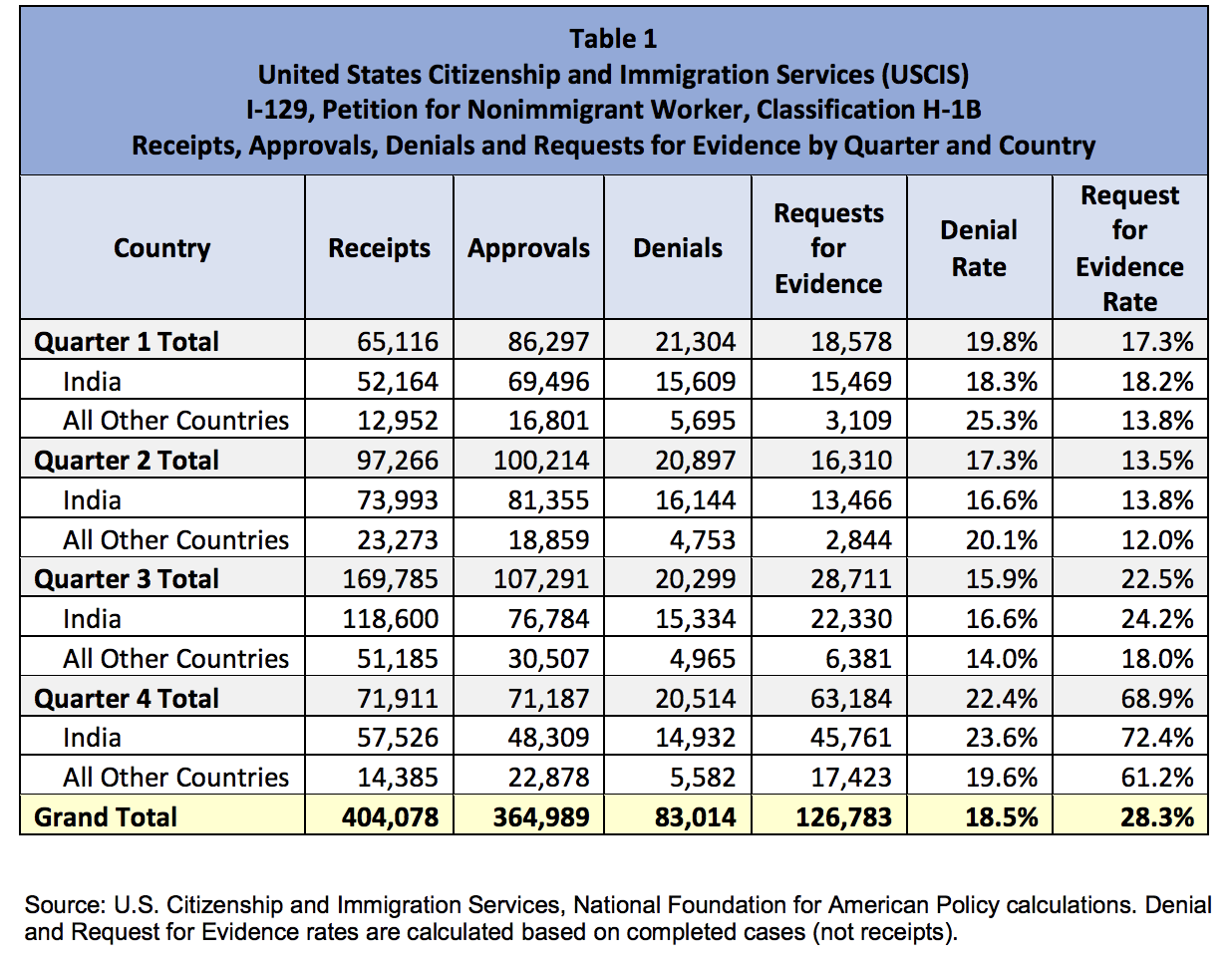
Beginning next year, the United States Citizenship and Immigration Services (USCIS) will launch a task force located in Los Angeles, designed to identify, detect, and prosecute individuals who have fraudulently gained United States Citizenship, for example by entering into a ‘sham’ marriage to obtain permanent residence, or engaging in other fraudulent activity, such as using a false identity to apply for permanent residence and/or naturalization.
USCIS has already begun to process of hiring lawyers and immigration officers who will review cases of individuals who have been deported, who the agency believes may potentially use a false identity to obtain permanent residence and/or citizenship. Such cases will be referred to the Department of Justice, who will then initiate the removal of individuals who have committed immigration fraud.
Of the denaturalization task force, USCIS Director L. Francis Cissna told reporters, “We finally have a process in place to get to the bottom of all these bad cases and start denaturalizing people who should not have been naturalized in the first place. What we’re looking at, when you boil it all down, is potentially a few thousand cases.”
The denaturalization task force will be funded by immigration application filing fees. The denaturalization task force will be primarily focused on targeting individuals who have used false identities to obtain immigration benefits.
 Visa Lawyer Blog
Visa Lawyer Blog