In this segment, we answer 5 of your most frequently asked questions received on our social media platforms and our website. Please remember that every case is different and every immigration journey is unique. You should not compare your situation to anyone else’s. We hope that our answers will provide you with further guidance while you embark on your immigration journey. If you have any further questions, please call our office to schedule a free first time consultation. We serve international clients and domestic clients in all 50 states. We thank you for your continued trust in our law office. For more information on the services we offer please click here.
Fiancé Visa
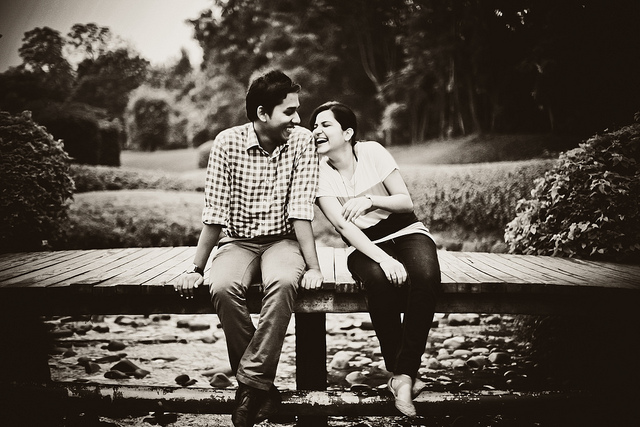
Q: I am a U.S. Citizen who is planning to marry a Moroccan citizen. I am interested in applying for the K-1 fiancé visa for him. The problem is that we have not met in person and it is hard for me to travel to his country because I am a single parent. I know one of the requirements for this visa is to meet in person. Are there any other visa options available to us since we have not met in person? I have heard of people obtaining waivers due to traveling hardships. Please advise.
A: Thank you for your question. This is a very common fiancé visa question. In order to file the K-1 fiancé visa you must meet the following requirements:
- You (the petitioner) are a U.S. citizen.
- You intend to marry within 90 days of your fiancé(e) entering the United States.
- You and your fiancé(e) are both free to marry and any previous marriages must have been legally terminated by divorce, death, or annulment.
- You met each other, in person, at least once within 2 years of filing your petition. There are two exceptions that require a waiver:
If the requirement to meet would violate strict and long-established customs of your or your fiancé(e)’s foreign culture or social practice.
2. If you prove that the requirement to meet would result in extreme hardship to you.
As indicated above there are only two exceptions that would allow you to seek a waiver of the K-1 visa two-year meeting requirement. The first requires the petitioner to demonstrate that compliance of the two-year meeting requirement would violate strict and long-established customs of either your fiancé’s foreign culture or social practice or of your own foreign culture or social practice. While it is difficult to prove this, it is not impossible, however the couple should be aware that substantial evidence is required to prove that either your or your fiancé’s culture explicitly prohibits you from meeting the two-year requirement. Of course this element is largely at odds with traditional Western norms and practices, therefore it is extremely difficult to explain to an immigration officer why you and your fiancé cannot meet in person before you are to be married. This waiver should only be considered in very limited circumstances.
 Visa Lawyer Blog
Visa Lawyer Blog